In today’s rapidly changing world, finding sustainable methods of food production is crucial for the well-being of our planet. One innovative solution that has gained popularity in recent years is aquaponics. Combining aquaculture (the cultivation of fish) with hydroponics (growing plants in water), aquaponics offers a symbiotic system that has numerous advantages in sustainable food production. By harnessing the natural processes of nutrient cycling and waste management, aquaponics minimizes the use of water and eliminates the need for synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides. In this article, we will explore the various benefits that aquaponics brings to the table, from its efficient use of resources to its potential to address food security challenges. So, if you’re interested in learning more about how aquaponics can play a vital role in sustainable agriculture, read on!
Increased Efficiency
Aquaponics offers several advantages that contribute to increased efficiency in sustainable food production. Firstly, aquaponic systems require significantly less water compared to traditional farming methods. The water in the system is recycled and recirculated, reducing the overall water usage. This conservation of water resources is crucial, especially in regions that face water scarcity and drought conditions.
Additionally, aquaponics eliminates the need for large areas of land, making it a space-efficient method of food production. By utilizing vertical systems and compact designs, aquaponic farms can produce a substantial amount of food in a limited space. This is particularly beneficial in urban areas where land availability is limited.
Furthermore, aquaponics optimizes resource utilization. The nutrient-rich water from the fish tanks is circulated to the plants, providing them with the necessary nutrients for growth. This symbiotic relationship between fish and plants ensures efficient utilization of resources, as the fish waste serves as a valuable source of nutrients for the plants. This closed-loop system minimizes waste and maximizes the overall efficiency of the farming process.
Environmental Benefits
Apart from increased efficiency, aquaponics also offers several environmental benefits. One of the significant advantages is the minimal reliance on synthetic fertilizers. Traditional farming methods often rely on chemical fertilizers to provide essential nutrients to plants. In contrast, aquaponics utilizes the waste produced by fish to naturally fertilize the plants. This eliminates the need for synthetic fertilizers, reducing the environmental impact associated with their production and use.
In addition, aquaponics requires lower energy consumption compared to traditional farming methods. The recirculating water and controlled environment in an aquaponic system minimize the energy required for irrigation and pest control. This reduction in energy consumption helps in conserving valuable resources and reduces the carbon footprint associated with food production.
Furthermore, aquaponics eliminates the need for chemical pesticides. Traditional farming methods often rely on chemical pesticides to protect crops from pests and diseases. However, these pesticides can have harmful effects on the environment and human health. In an aquaponic system, natural pest control methods such as beneficial insects and biological controls can be utilized, eliminating the need for chemical pesticides. This promotes a healthier and more sustainable approach to food production.
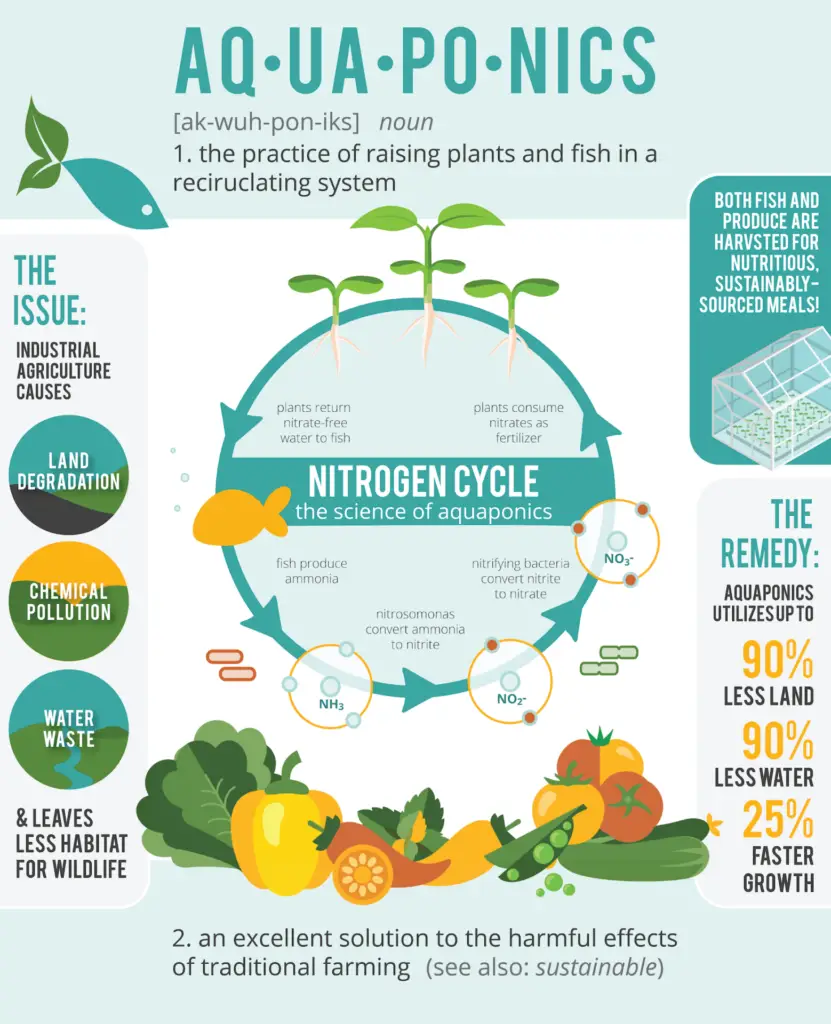
Water Conservation
Aquaponics is a water-efficient method of food production that prioritizes water conservation. The system operates on a recirculating water model, where water is continuously reused. This recirculation of water significantly reduces the overall water consumption in comparison to traditional farming, where water is often wasted or lost through irrigation.
Moreover, aquaponics minimizes water loss through evaporation. By utilizing enclosed systems or greenhouse structures, the water in the system is protected from direct exposure to the sun and external elements. This reduces evaporation, preventing unnecessary water loss and making aquaponics even more water-efficient.
Additionally, aquaponic systems contribute to water conservation by minimizing water pollution. The closed-loop system ensures that the water is continuously filtered and purified, removing any potential contaminants. As a result, the discharge from an aquaponic system is of high quality, with no harmful substances being released into the environment. This helps in maintaining the water quality and preserving the natural ecosystem.
Improved Crop Quality
One of the key advantages of aquaponics is the ability to create controlled and stable growing conditions, leading to improved crop quality. In traditional farming, crops are subjected to variations in weather conditions, which can adversely affect their growth and quality. However, in an aquaponic system, the environment can be precisely controlled, providing the plants with the ideal conditions for optimal growth.
Furthermore, aquaponics eliminates the risk of soil-borne diseases. In traditional farming, soil can harbor various pathogens and diseases that can affect the crops. Aquaponic systems do not use soil, eliminating the risk of soil-borne diseases. This ensures that the plants remain healthy and free from any disease, resulting in higher quality produce.
Moreover, aquaponically grown crops are known to have higher nutrient density compared to conventionally grown crops. The nutrient-rich water in the system provides the plants with an abundance of essential minerals and nutrients, resulting in crops that are more nutrient-dense. This makes aquaponically grown produce an excellent choice for individuals seeking nutritious and high-quality food options.
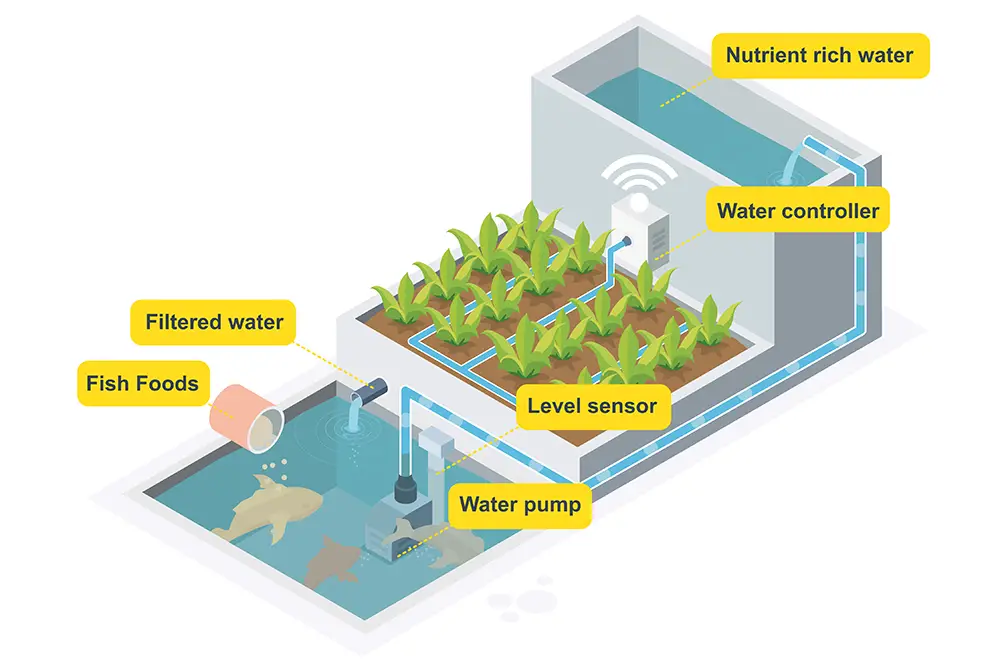
Year-Round Food Production
Aquaponic systems enable year-round food production, offering significant advantages over traditional farming methods that are limited by seasonal variations and adverse weather conditions. With the controlled environment provided in an aquaponic system, crops can be grown and harvested throughout the year.
The all-season harvesting capability of aquaponics ensures a continuous supply of fresh produce, irrespective of external weather conditions. This enables farmers to meet the increasing demand for food consistently and reliably, contributing to food security.
Additionally, aquaponics offers a continuous growth cycle. As plants are grown in nutrient-rich water and under controlled conditions, they tend to have faster growth rates compared to traditional farming. This allows for shorter growing cycles, resulting in faster and more frequent harvests. The ability to harvest multiple times in a single year significantly increases overall food production.
Furthermore, aquaponics eliminates the setbacks caused by weather-related factors such as droughts, floods, or extreme temperatures. With climate change becoming a growing concern, these weather-related setbacks can significantly affect traditional farming. However, aquaponics mitigates this risk by providing a controlled environment, ensuring consistent production regardless of external factors.
Higher Yield
Aquaponics facilitates optimized plant growth, leading to higher yields compared to traditional farming methods. The constant supply of nutrients provided by the fish waste in the system ensures that the plants have access to the necessary resources throughout their growth cycle. This optimal nutrition results in healthier, larger, and more productive plants, thereby increasing overall yield.
Moreover, aquaponics allows for increased crop density. As plants in an aquaponic system receive their nutrients directly from the water, they can be grown in closer proximity to one another. This vertical or compact growth arrangement allows for more plants to be cultivated in a given space. The higher crop density further contributes to higher yields and maximizes the productivity of the system.
Additionally, aquaponics enables more harvests per year compared to traditional farming methods. The fast growth rates and shorter growing cycles in an aquaponic system facilitate frequent harvests. This means that farmers can obtain multiple crop yields within a single year, maximizing the overall food production and increasing profitability.
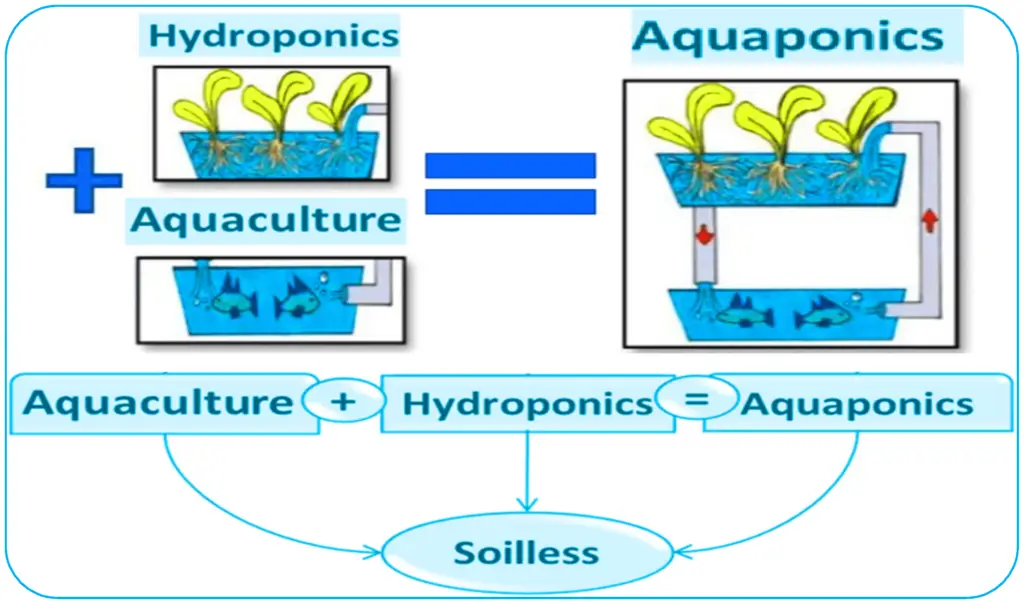
Minimal Carbon Footprint
Aquaponics offers a sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to food production with a minimal carbon footprint. One of the significant advantages in terms of environmental impact is lower greenhouse gas emissions. Traditional farming methods, such as the use of synthetic fertilizers and heavy machinery, contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. In contrast, aquaponics eliminates the need for synthetic fertilizers, reduces energy consumption, and minimizes carbon emissions. This makes aquaponics a climate-friendly option for sustainable food production.
Moreover, aquaponics reduces transportation distances. Fresh produce often needs to be transported long distances from the farms to the consumers, resulting in increased carbon emissions from transportation. However, with aquaponics, food can be grown in urban areas or close to consumers, minimizing the need for long-distance transportation. This reduces the carbon footprint associated with food distribution and promotes a more sustainable and localized food system.
Additionally, aquaponics eliminates soil degradation, which is a common issue in traditional farming. The continuous exploitation of soils in conventional agriculture can lead to erosion, nutrient depletion, and loss of soil fertility. In aquaponics, there is no soil involved, eliminating the risk of soil degradation. This sustainable farming method prioritizes the health and preservation of the environment, ensuring a minimal negative impact on the ecosystem.
Diverse Food Production
Aquaponics allows for diverse food production, offering the opportunity to grow various fish and plant species in a single system. Aquaponic farms can cultivate a wide range of fish, such as tilapia, trout, or catfish, depending on the climate and market demand. This diversification in fish species allows farmers to cater to different customer preferences and expand their product offerings.
Moreover, aquaponics provides flexibility in crop choices. Various crop varieties, including leafy greens, herbs, fruits, and vegetables, can be grown in an aquaponic system. Farmers can choose crops that are suitable for their region, market demand, and personal preferences. This flexibility allows for experimentation and adaptation to changing market trends, enabling farmers to meet the diverse dietary needs of consumers.
Furthermore, aquaponics provides an opportunity for organic farming. The absence of synthetic fertilizers and chemical pesticides in aquaponics aligns with the principles of organic farming. By adopting organic practices, aquaponic farmers can produce organic-certified fish and crops, appealing to consumers who prioritize organic and sustainable food options. This opens up new markets and opportunities for farmers to tap into the growing demand for organic produce.

Food Security
Aquaponics plays a crucial role in ensuring food security by promoting local and self-sustainable food production. As aquaponics utilizes a closed-loop system, it reduces reliance on external inputs and resources. This self-sustaining nature of aquaponics allows farmers to produce food locally, eliminating the need for extensive food imports.
Additionally, aquaponics reduces vulnerability to climate change. With weather patterns becoming increasingly unpredictable, traditional farming is at risk of crop failures and yield losses. Aquaponics provides a climate-controlled environment, enabling farmers to produce food consistently and reliably despite extreme weather conditions. This resilience to climate change ensures a continuous food supply and reduces vulnerability to external factors.
Furthermore, aquaponics decreases reliance on imports. Many regions heavily rely on food imports to meet their dietary needs, making them vulnerable to disruptions in the global food supply chain. By implementing aquaponic systems locally, communities can produce a significant portion of their food requirements, reducing dependence on imports. This strengthens food security and enhances the resilience of local food systems.
Economic Viability
Aquaponics offers economic viability through its potential for commercial-scale production. As the demand for fresh, sustainably produced food increases, aquaponic farms have the opportunity to scale up their operations and cater to larger markets. With advancements in technology and knowledge, commercial aquaponic systems can achieve significant yields, contributing to the profitability and economic success of farmers.
Moreover, aquaponics is a cost-effective method of food production. While the initial setup costs of an aquaponic system may be higher than traditional farming methods, the long-term operational costs are relatively low. The closed-loop system’s efficiency reduces the need for inputs such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides, resulting in cost savings over time. Additionally, the continuous growth and frequent harvests in aquaponics increase revenue streams, making it financially viable for farmers.
Furthermore, aquaponics provides new job opportunities. With the expansion of aquaponic farms, there is a growing demand for skilled labor to manage and operate these systems. The development of aquaponics opens up employment opportunities in various roles, including farm managers, technicians, and sales and marketing personnel. This contributes to job creation and supports the growth of local economies.

